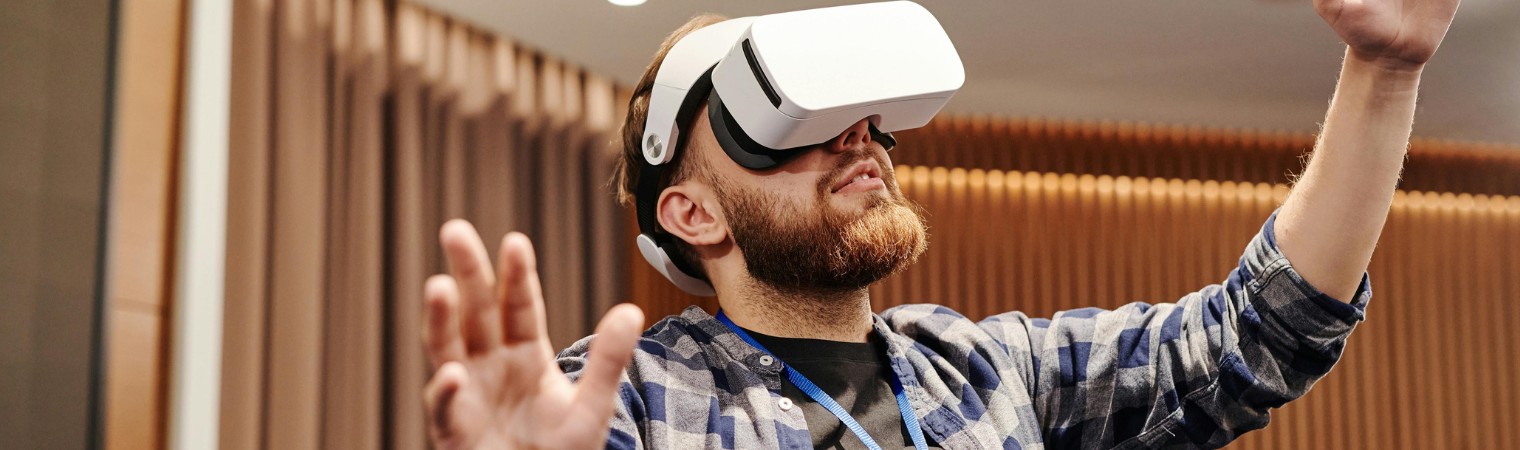
The concept of the Metaverse has transcended its origins in science fiction and is rapidly becoming a tangible reality. This virtual universe, often likened to the internet but in 3D, holds the promise of revolutionizing how we work, socialize, and interact online. Here’s a comprehensive look at what the Metaverse entails and how it is evolving from a visionary concept into a practical application.
What is the Metaverse?
The Metaverse refers to a collective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual reality. In essence, it’s a network of interconnected virtual worlds, augmented by digital assets and user-generated content, where individuals can interact with each other and digital environments in real-time.
Origins and Evolution
The term “Metaverse” was coined by Neal Stephenson in his 1992 science fiction novel “Snow Crash,” where it described a virtual reality-based successor to the internet. Since then, the idea has captured the imagination of technologists and futurists alike, paving the way for its development in various forms over the decades.
Technological Foundations
Advancements in virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain technology, and high-speed internet have laid the groundwork for the Metaverse’s emergence. These technologies enable immersive experiences, digital ownership (through NFTs), and seamless connectivity across virtual spaces.
Key Components of the Metaverse
- Virtual Worlds: These are immersive digital environments where users can interact with each other and objects, often using avatars to represent themselves.
- Digital Assets: NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) play a crucial role in the Metaverse by allowing ownership of virtual land, virtual goods, art, and other digital assets.
- Social Interaction: The Metaverse fosters socialization through virtual gatherings, events, and activities, mirroring real-world interactions but in a digital space.
Applications Across Industries
The potential applications of the Metaverse extend beyond entertainment and gaming to various industries:
- Education: Virtual classrooms and interactive learning environments.
- Business: Virtual meetings, conferences, and remote collaboration spaces.
- Healthcare: Virtual simulations for training, therapy, and remote consultations.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Metaverse presents exciting opportunities, several challenges must be addressed.
Technical Hurdles
Achieving seamless interoperability and scalability across virtual platforms.
Privacy and Security
Safeguarding user data and ensuring safe interactions within virtual environments.
Accessibility
Ensuring equitable access to the Metaverse for all users, regardless of their technological capabilities or resources.
Future Outlook
The development of the Metaverse is gaining momentum, driven by tech giants, startups, and innovators exploring its vast potential. As technologies continue to evolve and societal acceptance grows, the Metaverse is poised to redefine digital interactions and experiences in the years to come.
Conclusion
The Metaverse represents a convergence of virtual reality, digital assets, and social interaction, transforming the way we perceive and engage with digital environments. From its conceptual roots in science fiction to its current trajectory as a viable technological reality, the Metaverse holds promise for reshaping industries, fostering new forms of creativity, and connecting people on a global scale. As developments unfold, the Metaverse stands at the forefront of innovation, offering a glimpse into the future of digital connectivity and immersive experiences.
Tags:
Digital TransformationTech IndustryTech TrendsAuthor - Imran Khan
Imran Khan is a seasoned writer with a wealth of experience spanning over six years. His professional journey has taken him across diverse industries, allowing him to craft content for a wide array of businesses. Imran's writing is deeply rooted in a profound desire to assist individuals in attaining their aspirations. Whether it's through dispensing actionable insights or weaving inspirational narratives, he is dedicated to empowering his readers on their journey toward self-improvement and personal growth.